

The highest prevalence of 47.4 % is in preschool-age children while the lowest prevalence of 12.7 % is in men. Globally, 1.62 billion people are anemic, corresponding to 24.8 % of the global population. It occurs at all stages of life, especially in pregnant women and children. Īnemia has a high prevalence and is considered a public health problem affecting developing and developed countries. Anemia is associated with increased perinatal mortality, child morbidity and mortality, impaired mental development, immune incompetence, increased susceptibility to lead poisoning, and decreased performance at work. It is caused by either an excessive destruction or diminished production of red blood cells. This leads to the blood not being able to meet the body’s physiological needs. The findings suggest that a high incidence of anemia is likely to occur in patients with poorly controlled diabetes and in patients with diabetes and renal insufficiency.ĭeficiency in the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood due to a diminished erythrocyte mass or reduction in the hemoglobin (Hb) concentration of the blood may indicate anemia. Finally, a significant association between hemoglobin concentration and fasting blood glucose was also observed in the cases. Renal insufficiency determined by serum creatinine level of >1.5 mg/dL, estimated glomerular filtration rate <60 ml/minute/1.73 m 2, and erythropoietin levels was also observed to be high in the cases (54.0 % with mean creatinine concentration of 3.43☑.73 and erythropoietin 6.35☑.28 mIU/mL). Of the patients with diabetes, 84.8 % had a hemoglobin concentration that was significantly less (males 11.16☑.83 and females 10.41☑.49) than the controls (males 14.25☑.78 and females 12.53☑.14).

ResultsĪ high incidence of anemia was observed in the cases. The prevalence of anemia was then determined statistically.
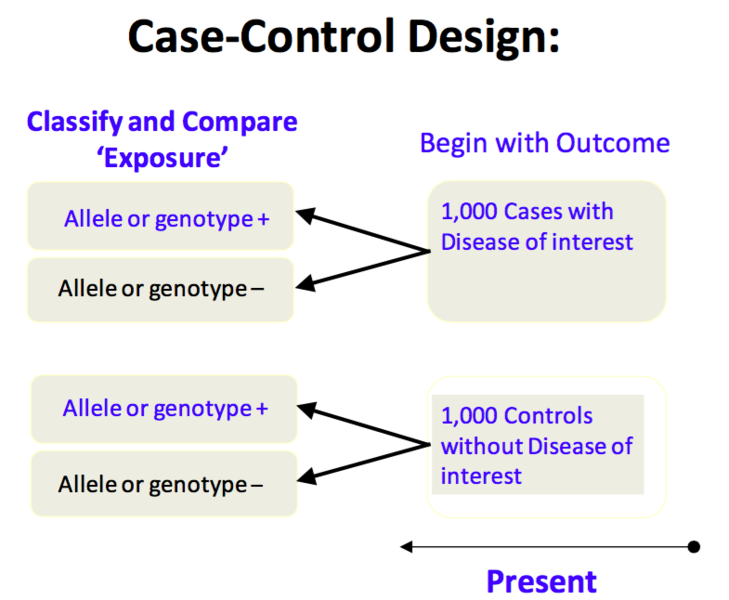
#Case control study full#
Participants’ blood samples were analyzed for fasting blood glucose, full blood count and renal function tests among others. MethodsĪ total of 100 (50 with type 2 diabetes and 50 controls) participants were recruited for our study. The aim of this study was therefore to determine the prevalence of anemia among patients with type 2 diabetes. Understanding the pathogenesis of anemia associated with diabetes may lead to the development of interventions to optimize outcomes in these patients. Other studies have also identified anemia as a risk factor for the need for renal replacement therapy in diabetes. Several reports have indicated that anemia mostly occurs in patients with diabetes with renal insufficiency while limited studies have reported the incidence of anemia in people with diabetes prior to evidence of renal impairment. Anemia is defined as a reduction in the hemoglobin concentration of blood, which consequently reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of red blood cells such that they are unable to meet the body’s physiological needs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
